What Are 3 Aspects That Are Wrong With The Fire Service
Burn down Prevention
The safest way to bargain with burn is to prevent information technology.
Under Section 19 of the Safety, Health and Welfare at Piece of work Act 2005 (the 2005 Human activity) every employer shall identify hazards, assess risks and have a written take a chance cess, including any unusual or other risks. To comply with Section 19, employers are required to carry out gamble assessments and to record these in the Condom Statement. A fire safetygamble cess should be conducted. Fire prevention should form role of this.
A fire safety risk assessment should include
Dorsum to top
Fire Prevention
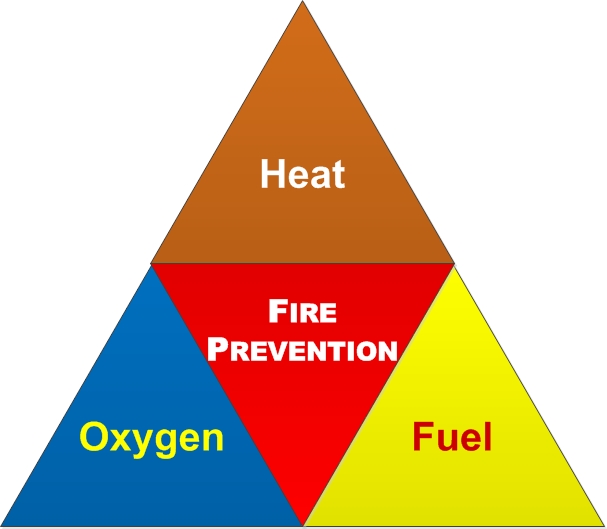 | The Fire Prevention Triangle - Oestrus, Oxygen and Fuel A fire needs three elements - heat, oxygen and fuel. Without oestrus, oxygen and fuel a fire will non start or spread. A primal strategy to prevent burn is to remove 1 or more than of heat, oxygen or fuel. The hazard assessment should include detail on all iii elements to minimise the take chances of a burn starting/ spreading. |
A fire prevention strategy and a fire risk assessment should include particular and a full consideration of all of the problems - including issues arising from heat, oxygen and fuel. Advice on these 3 elements follows. This communication is not exhaustive and is given in no particular guild.
Back to top
Heat
Heat can be generated by piece of work processes and is an essential part of some processes such every bit cooking. This heat must be controlled and kept abroad from fuel unless carefully controlled. Heat generated as a by-product of a process must be dealt with properly.
 | | | | | |
Back to top
Heat Safeguards
|  |
Back to summit
| | Smoking |
|  |
Back to top
| | Plant and Equipment |
Plant and equipment which is not properly maintained can cause fires.
- Ensure all work equipment protects against catching fire or overheating
- Ensure proper housekeeping, such as preventing ventilation points on machinery condign chock-full with dust or other materials - causing overheating
- Take electric equipment serviced regularly by a competent person to foreclose sparks and fires
- Properly make clean and maintain heat producing equipment such as burners, heat exchangers, boilers (inspected and tested yearly), ovens, stoves, and fryers. Require storage of flammables abroad from this equipment.
- Use a planned maintenance programme to properly maintain institute and equipment. Review your programme if you already have one.
- A planned maintenance programme should deal with
- frictional heat (caused by loose drive belts, bearings which are non properly lubricated or other moving parts)
- electrical malfunction
- flammable materials used in contact with hot surfaces
- leaking valves or flanges which allow seepage of flammable liquids or gases
- static sparks (perchance due to inadequate electrical earthing)
Portable Heaters
- Exercise not employ portable heaters unnecessarily.
- They should accept emergency tip-over switches, and thermostatic limiting controls.
- Turn them off if people go out the room or are going to sleep
- Ensure they are 1M away from anything that can burn
- Do not utilise them to dry apparel
Back to acme
| | Hot Work |
| Hot work often arises from construction and/ or maintenance activities. Hot piece of work is work that might generate sufficient estrus, sparks or flame to cause a fire. Hot work includes welding, flame cutting, soldering, brazing, grinding and other equipment incorporating a flame, east.one thousand. tar boilers, etc. Hot piece of work tin can be very dangerous and stringent controls must be in place. |  |
- Identify all hot piece of work
- But allow hot work if no satisfactory alternative
- Ensure relevant contractors are enlightened of hot piece of work procedures and controls
- Utilise a hot work allow system including
- burn-resistant protective habiliment
- clear responsibleness
- logging and audit processes
- routine checking and supervision
- item to be worked on removed to safety area
- remove or protect combustible or combustible materials
- preclude, suppress and control sparks
- prevent, suppress and control oestrus
- provision of and preparation on suitable fire-fighting equipment
- provision of a divide person to fire-watch and use fire-fighting equipment – the burn watcher
- detail precautions for special risks, east.g. confined space
- leave workplace clean and rubber
- final cheque of expanse at least sixty minutes after completed job and certainly prior to premises beingness vacated
Back to top
| | Electrical condom |
- All electrical equipment and installations designed, constructed, installed, maintained, protected, and used to forestall danger
- Get a qualified electrical contractor to carry out installation and repairs to electrical equipment and fittings
- Maintain proper pest control to avoid rodent impairment to electric wiring and equipment
| |
Back to summit
| | Arson |
Deliberately started fires pose very significant risks to all types of workplace.
The possibility of arson should exist considered every bit a component of your risk assessment and it is one that y'all tin do much to command. The bulk of deliberately started fires occur in areas with a known history of vandalism or fire-setting. Typically, local youths low-cal the fires outside the bounds equally an act of vandalism, using materials found nearby. Advisable security measures, including the protection of stored materials and the efficient and prompt removal of rubbish, can therefore do much to alleviate this particular problem.
You should therefore seek advice from the local Gardaí or the fire authority who will involve the other agencies as appropriate. Occasionally, arson attacks in the workplace are committed by employees or ex-employees. Employers and other workers should be aware of this potential threat and be alert for early on signs, such as a series of unexplained small fires. Once again, the Gardaí or the local fire authorisation tin can provide farther useful guidance.
- Provide acceptable security: exterior/interior lighting, intrusion alarms, guard service, well-secured admission openings
- Prevent admission past unauthorised personnel
- Keep flammables properly stored and secured
Back to tiptop
Oxygen
Oxygen gas is used
- in welding, flame cutting and other similar processes
- for helping people with animate difficulties
- in hyperbaric chambers as a medical handling
- in decompression chambers
- for food preservation and packaging
- in steelworks and chemical plants
 | ||||
| | ||||
 | ||||
The air we breathe contains virtually 21% oxygen. Pure oxygen at loftier pressure, such equally from a cylinder, tin react violently with common materials such equally oil and grease. Other materials may catch burn down spontaneously. Nearly all materials including textiles, safety and fifty-fifty metals volition burn vigorously in oxygen.
With even a small increase in the oxygen level in the air to 24%, it becomes easier to start a fire, which will then fire hotter and more fiercely than in normal air. Information technology may exist almost impossible to put the burn out. A leaking valve or hose in a poorly ventilated room or confined space tin quickly increase the oxygen concentration to a dangerous level.
The chief causes of fires and explosions when using oxygen are
- oxygen enrichment from leaking equipment
- use of materials not compatible with oxygen
- use of oxygen in equipment not designed for oxygen service
- incorrect or devil-may-care operation of oxygen equipment
(Information from HSE UK - Take intendance with oxygen - Burn down and explosion hazards in the apply of oxygen - eight pages)
| | Oxygen Safeguards |
- Ensure employees are aware of their responsibleness to report dangers
- Encounter safeguards in the Lawmaking of Practice for Working in Confined Spaces
- Oxygen should never be used to "sweeten" the air in a confined infinite
- Where oxygen is used,
- follow prophylactic advice from the supplier
- follow the safeguards on the safety information canvas
- keep the safety information sheet readily available
- Be enlightened of the dangers of oxygen if in doubt, ask
- Prevent oxygen enrichment past ensuring that equipment is leak-tight and in proficient working order
- Check that ventilation is adequate
- E'er use oxygen cylinders and equipment carefully and correctly
- Always open oxygen cylinder valves slowly
- Do not smoke where oxygen is being used
- Never use replacement parts which have not been specifically canonical for oxygen service
- Never use oxygen equipment to a higher place the pressures certified by the manufacturer
- Never apply oil or grease to lubricate oxygen equipment
- Never use oxygen in equipment which is not designed for oxygen service
- Operators of locations storing big amounts of oxidising substances have duties under the Command of Major Accident Hazards Involving Dangerous Substances Regulations (COMAH Regulations)
(Some information from HSE United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland - Take care with oxygen - Fire and explosion hazards in the use of oxygen - 8 pages)
Dorsum to height
Fuel
Workplaces in which large amounts of flammable materials are displayed, stored or used can present a greater hazard than those where the amount kept is small.
In relation to burn, fuel consists of flammable material. Flammable fabric is material that burns readily in a normal atmosphere. Flammable materials include flammable liquids (eastward.g. petrol), flammable gasses (e.g. propane and butane) and combustible solids (e.g. charcoal, paper). It is of import to identify all flammable materials that are in your workplace so that proper controls tin be put in place.
 | ||||
 | ||||
| | ||||
| | | | ||
Great care is required in the storage, handling and use of flammable materials. Safety Data sheets may provide detailed advice.
Fuel Safeguards
- Ensure employees are aware of their responsibleness to report dangers
- Follow the Authority'southward advice on LPG
- Follow the Authority's advice on explosive atmospheres and use the Guide to the Safety, Health and Welfare at Work (General Awarding)Regulations2007 - Part 8:Explosive Atmospheres
- Use the Code of Practice For Avoiding Danger From Surreptitious Services
- Use Bord Gáis Networks rubber webpage including Dial Before You Dig
- Ensure furnishings and fittings in places of assembly comply with the Lawmaking of Practice for Burn Rubber of Effects and Fittings in Places of Assembly
- Let no timber lining on ceiling, corridor walls/ ceilings or stairways (but exception is Class 0 MDF)
- Take care if placing notice boards in escape corridors/ routes as any paper on the board could exist fuel in the outcome of a fire
- Where there is a possibility of the presence of flammable gas/ vapour, deport a full risk assessment and consider the demand for gas detection equipment
- Where gas detection equipment is needed, ensure information technology is properly installed, maintained and serviced
- Operators of locations storing larger amounts of substances with flammable or explosive properties have duties under the COMAH Regulations. (Note that the highly flammable liquid threshold is 10 tonnes, while Hydrogen and Acetylene are both at 5 tonnes.)
Back to superlative
| | Combustible materials |
- Place all combustible materials so that proper controls can be put in place
- Place use of substances with combustible vapours (e.thousand. some adhesives)
- Reduce quantities of combustible materials to the smallest amount necessary for running the business organisation and keep away from escape routes
- Supercede highly combustible materials with less flammable ones
- Store remaining stocks of highly flammable materials properly outside, in a separate building, or separated from the main workplace by burn down-resisting structure
- Provide clearly marked divide storage for flammable chemicals, gas cylinders, and waste materials
- Train employees on safety storage, treatment and use of flammable materials
- Keep stocks of office stationery and supplies and combustible cleaners' materials in divide cupboards or stores. They should be fire-resisting with a fire door if they open onto a corridor or stairway escape road
- Catering and hospitality premises – see relevant sections of Prophylactic Hospitality, eastward.1000. sections 1.thirteen LPG/ Gas Prophylactic, 1.15 Fire Safe, vi.eleven Flambé Lamps
- The US Occupational Safety and Health Administration has a webpage on combustible grit with tabs, beginning with information for users unfamiliar with flammable dust hazards
- Come across our information sheet on dwelling heating oil (ii pages), and our data sheets on storage of hazardous chemicals in Warehouses and Drum Stores (4 pages) and Laboratories (4 pages)
Work on Gas Mains
Run across the press release "Construction firm fined €40,000 later on workers sustain serious burn injuries" and the UK commodity "PPE saved worker from moreserious burn injuries"
- This is highly specialised work and a detailed adventure assessment must be conducted
- Detailed work instructions must be put in place
- Construction and Maintenance workers – see advice on planning construction and maintenance activities at www.hsa.ie, eastward.g. precautions to avert underground services and/or overhead lines
- Advice should be sought from the gas supplier as needed
- Workers must be properly trained and supervised
Dorsum to top
| | Flammable liquids |
| Combustible liquids tin can present a significant risk of fire. Vapours evolved are usually heavier than air and tin can travel long distances, so are more than likely to reach a source of ignition. Liquid leaks and dangerous vapours tin can arise from faulty storage (bulk and containers), establish and process - design, installation, maintenance or use. Ignition of the vapours from flammable liquids remains a possibility until the concentration of the vapour in the air has reduced to a level which volition not support combustion. | |
- The quantity of flammable liquids in workrooms should be kept to a minimum, normally no more a half-day's or one-half a shifts supply
- Flammable liquids, including empty or part-used containers, should be stored safely. Pocket-sized quantities (Tens of Litres) of flammable liquids can exist stored in the workroom if in closed containers in a burn down-resisting (e.g. metal), bin or cabinet fitted with means to contain whatsoever leaks
 | Metal Storage for Flammable Chemicals to EN-14470-1
|
- Flammable liquids should not be decanted within the store. Decanting should accept place in a well-ventilated area set up aside for this purpose, with appropriate facilities to contain and clear up any spillage
- Container lids should always be replaced after use, and no container should ever be opened in such a way that it cannot exist safely resealed
- Flammable liquids should exist stored and handled in well ventilated atmospheric condition. Where necessary, additional properly designed frazzle ventilation should be provided to reduce the level of vapour concentration in the air
 | Containers for Flammable Liquid
|
- At that place should be no potential ignition sources in areas where flammable liquids are used or stored and flammable concentrations of vapour may be present at any time. Any electrical equipment used in these areas, including burn down alarm and emergency lighting systems, needs to be suitable for use in flammable atmospheres
- Petrol Stations – run across Wetstock Inventory Control for Petrol Stations at www.hsa.ie
- Run across our information sheet on dwelling house heating oil (ii pages), and our information sheets on storage of hazardous chemicals in Warehouses and Pulsate Stores (4 pages) and Laboratories (4 pages)
- Run across our webpage on Chemicals Adventure Cess for advice on completing a chemical agents take a chance assessment
Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs)
The utilise of plastic and composite intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) for liquid storage has increased. They take a number of advantages over traditional steel drums, in particular; resistance to corrosion, efficient storage space employ and ease of emptying when a valve is fitted. Plastic IBCs are used for hydrocarbons for: wastes; fuels such as diesel; solvents such as white spirit; lubricants; edible oils etc.
| A number of serious fires in the UK started or spread because of the use plastic IBCs for combustible liquids. A characteristic of these fires was the rapid release of liquid from IBCs, inadequacy of bunding and impairment acquired as a upshot of the unconfined catamenia of called-for liquid. This data is from HSE UK's communication on Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs) which includes a very helpful video. The Chemical Business Association and the Solvent Industry Association in consultation with the HSE Uk have produced Guidance for the storage of liquids in intermediate bulk containers (22 pages) |  |
Plastic components of IBCs are easily ignited. Liquid loss from IBCs can be rapid and consummate. In a fire, all of the liquid in unclad IBCs on level footing is probable to exist released rapidly (in 5-x minutes) and tin produce large spreading pool fires. Ullage explosions can exist extremely unsafe for anyone trying to fight the fire. Unless composite IBC blueprint can reduce the rate of liquid drainage in fires, the potential of fires continues to be very serious.
- IBC users should exist aware of the risks
- Take chances assessments for IBC storage should exist based on the premise that liquid loss will be rapid and complete
- Segregate IBCs and drums to avert rapid catastrophic failure of drums and associated fireballs and projectiles
- Kerbs and partitions in storage areas may be useful in checking the menstruation of liquid and spread of burn down
- For partitions to be constructive, drainage must be carefully controlled
- All processes introducing a risk of ignition should be eliminated or tightly controlled
- Strict control of readily ignitable material is required
- IBC storage areas should exist secure to deter coincidental vandalism
- Sites with large stocks of IBCs should consider drainage in the event of fire
- If at that place are sensitive targets nearby, substantial bunding may exist required
- Manufacturers and re-conditioners should provide articulate information on the potential behaviour of IBCs in fire
- Manufacturers should explore improvements in design
Dorsum to top
| | Cleanliness and housekeeping |
| |
- In catering, clean ventilation ducts on a regular footing to prevent grease build-up
- Combustible or combustible rubbish should not be stored, fifty-fifty as a temporary measure, in escape routes such as corridors, stairways or lobbies, or where it tin come into contact with potential sources of heat
- Parts of the workplace which are not normally occupied, such as basements, shop rooms and any area where a fire could grow unnoticed, should exist regularly inspected and cleared of non-essential flammable materials and substances. You should also protect such areas against entry past unauthorised people
- If the workplace has waste or derelict land nearby, you should keep any undergrowth under control then that a fire cannot spread through dry grass, for example
- There should be no potential ignition sources in areas where flammable liquids are used or stored and flammable concentrations of vapour may be present at any time. Whatever electrical equipment used in these areas, including fire alarm and emergency lighting systems, needs to be suitable for apply in combustible atmospheres
 | Metal Container for Cloths Contaminated with Combustible Solvents
|
Dorsum to top
| | Safety Data Sheets |
| Prophylactic data sheets provide useful data on chemicals and handling, storage and emergency measures. A safe information sheet should exist provided with whatever chancy chemical and includes useful data. Section two gives details on the hazards of the chemical and the potential effects and symptoms resulting from use. The information in this section must be consistent with the information on the characterization. Section 5 gives specific information on fighting a fire caused by the chemic, including the most suitable extinguishing media and protective equipment. Section 7 contains details on how to handle and store the chemical safely. Section 10 contains details of whatsoever hazardous reactions that may occur if the chemical is used under certain conditions. Section fourteen contains information relating to the transportation of the chemical. Section 16 gives any other data relevant to the chemical e.thou. training advice. |  |
- Handle material in accordance with the advice on the safe information sheet
- Proceed safety information sheets readily bachelor
- Proceed safety information sheets safely bachelor in the issue of a fire and so that the information is available for emergency services
Back to top
Fire Prevention Diagram
This diagram gives an overview of fire prevention for workplaces
 | | | | |
 | | |||
| |  | |||
 | | |||
| | | | ||
Back to tiptop
Go to
What Are 3 Aspects That Are Wrong With The Fire Service,
Source: http://www.hsa.ie/eng/topics/fire/fire_prevention/
Posted by: simpsonprinnexparm.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are 3 Aspects That Are Wrong With The Fire Service"
Post a Comment