Which Of The Following Scenarios Illustrates Denial Of Service (Dos), A Type Of Security Loss?
What Is a DDoS Assault
and How Does It Work?
What Is a DDoS Attack and How Does It Work?
The Information technology industry has recently seen a steady increment of distributed deprival of service (DDoS) attacks. Years agone, DDoS attacks were perceived as modest nuisances perpetrated by novice attackers who did it for fun and it was relatively easy to mitigate them. Unfortunately, that state of affairs is no more. DDoS attacks are now a sophisticated activity, and in many cases, big business.
InfoSecurity Magazine reported 2.9 million DDoS attacks in Q1 of 2021, an increase of 31% over the aforementioned menstruum in 2020.
DDoS attacks rose 31% in Q1 2021 over the same flow in 2020, to 2.9 one thousand thousand attacks
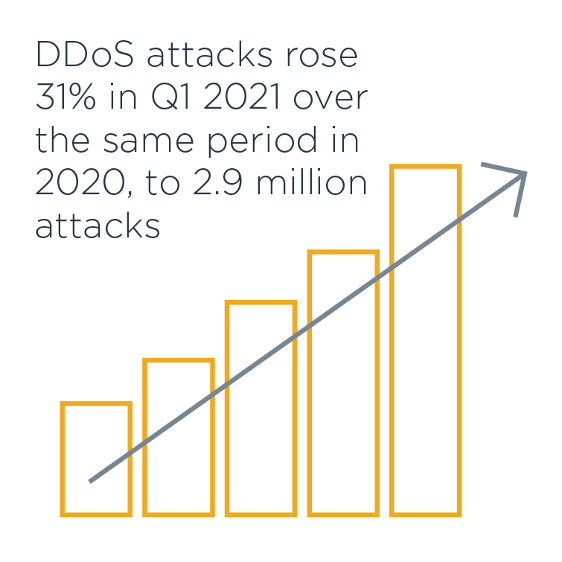
In contempo years, we take seen an exponential increase in DDoS attacks that accept incapacitated businesses for pregnant amounts of time.
- In February of 2020, Amazon Spider web Services (AWS) suffered a DDoS attack sophisticated enough to keep its incident response teams occupied for several days likewise affecting customers worldwide.
- In Feb of 2021, the EXMO Cryptocurrency exchange cruel victim to a DDoS attack that rendered the organization inoperable for almost five hours.
- Recently, Australia experienced a significant, sustained, state-sponsored DDoS attack.
- Kingdom of belgium too became a victim of a DDoS attack that targeted the country's parliament, police services and universities.
Hundreds of thousands of unnamed, undocumented, yet successful DDoS attacks continue daily. In fact, it is these attacks that are the about effective and costly. The DDoS upwards trend promises to proceed, putting IT pros with mitigation skills in high need.
Raging IT Warfare: What Is a DDoS Attack?
Despite becoming more common, DDoS attacks can be quite avant-garde and hard to combat. Only what exactly is a DDoS assault and what does DDoS stand for?
DDoS is brusk for distributed denial of service. A DDoS attack occurs when a threat player uses resources from multiple, remote locations to attack an organization's online operations. Commonly, DDoS attacks focus on generating attacks that manipulate the default, or fifty-fifty proper workings, of network equipment and services (e.g., routers, naming services or caching services). In fact, that's the main trouble.
Sophisticated DDoS attacks don't necessarily have to accept advantage of default settings or open up relays. They exploit normal behavior and take advantage of how the protocols that run on today's devices were designed to run in the first identify. In the same way that a social engineer manipulates the default workings of human communication, a DDoS attacker manipulates the normal workings of the network services we all rely upon and trust.
When a DDoS attack takes place, the targeted organization experiences a crippling interruption in i or more of its services considering the attack has flooded their resources with HTTP requests and traffic, denying access to legitimate users. DDoS attacks are ranked as ane of the top four cybersecurity threats of our time, amongst social engineering, ransomware and supply chain attacks.

Modern Warfare: Fugitive Confusion Almost DDoS Attacks
Information technology's relatively easy to confuse DDoS attacks with other cyberthreats. In fact, there is a significant lack of knowledge amid IT pros and fifty-fifty cybersecurity professionals concerning exactly how DDoS attacks work.
In a DDoS set on, cybercriminals take reward of normal behavior that occurs between network devices and servers, oftentimes targeting the networking devices that found a connectedness to the internet. Therefore, attackers focus on the border network devices (east.m., routers, switches), rather than individual servers. A DDoS set on overwhelms the network's pipe, (the bandwidth) or the devices that provide that bandwidth.
Hither's a useful analogy: Imagine that several people call yous simultaneously so that you lot can't make or receive telephone calls or apply your telephone for any other purpose. This problem persists until you block those calls through your provider.
Notice that you lot don't fix, upgrade or otherwise make adjustments to your bodily mobile device. Instead, yous fix the connexion between the attackers and your phone by using your mobile phone provider's blocking service.
A like thing happens during a DDoS attack. Instead of modifying the resource that is being attacked, you apply fixes (otherwise known as mitigations) betwixt your network and the threat thespian.

DDoS vs. DoS Attacks: What'southward the Difference?
It'southward important to avoid confusing a DDoS (distributed denial of service) assault with a DoS (deprival of service) attack. Although but one word separates the two, these attacks vary significantly in nature.
- Strictly defined, a typical DDoS set on manipulates many distributed network devices in between the attacker and the victim into waging an unwitting attack, exploiting legitimate behavior.
- A traditional DoS attack doesn't utilize multiple, distributed devices, nor does information technology focus on devices betwixt the attacker and the organization. These attacks also tend not to apply multiple net devices.
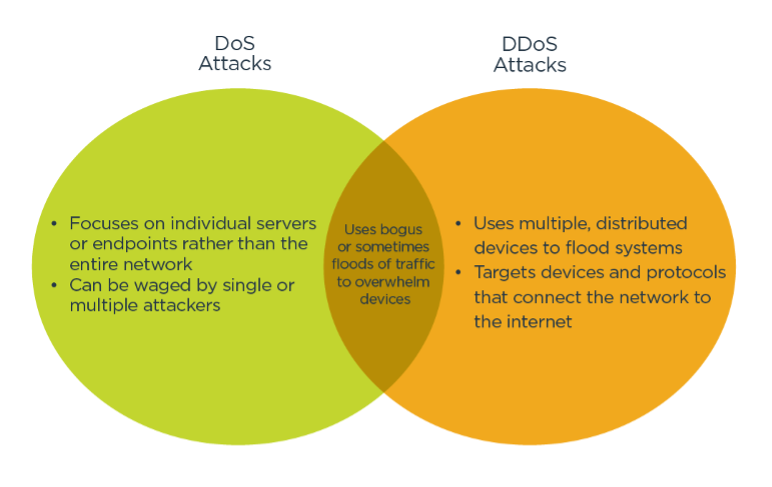
Typical DoS attacks can include the post-obit:
- Single-source SYN floods: This occurs when an attacker uses a single system to issue a flood attack of SYN packets, manipulating the typical TCP three-manner handshake. For example, a SYN flood someone might generate using a Kali Linux reckoner is non a truthful DDoS attack because the attack beingness made is only coming from ane device. This is the case even if the assaulter uses IP address spoofing. A true DDoS attack is generated by network-level devices, for network-level devices. In other words, you lot use multiple routers or Memcached servers to attack a network.
- The "ping of death": Years ago, some network drivers independent flawed code that would crash a organization if it received an ICMP packet that independent certain parameters.
- The slow loris attack: The deadening loris assail is oftentimes chosen a DDoS attack, merely because the attack targets a specific server (in this example, a spider web server) and usually does non use intermediate networking devices, information technology is typically a traditional DoS set on.
Each of the above DoS attacks have advantage of software or kernel weaknesses in a item host. To resolve the outcome, yous fix the host, and/or filter out the traffic. If you tin upgrade a server to mitigate an attack, then it doesn't qualify as a traditional DDoS attack.
Recall, in a DDoS attack, the threat actor adopts a resource consumption strategy. This strategy involves using what appears to be legitimate requests to overwhelm systems which are, in fact, not legitimate, resulting in system problems.
Assault Strategy: Types of DDoS Attacks
At that place are 3 full general types of DDoS attacks.
Awarding Layer attacks target the actual software that provides a service, such as Apache Server, the most popular web server on the cyberspace, or any application offered through a cloud provider. This is the most mutual form of DDoS attack and is often referred to every bit Layer 7 attacks, subsequently the corresponding number of the application layer in the OSI/RM.
This occurs when an attack consumes the resources of critical servers and network-based devices, such as a server's operating organisation or firewalls. While those resources are overwhelmed, balancers are loaded. Protocol attacks often include manipulating traffic at layers iii and 4 of the OSI/RM (the network and transport layers, respectively). This is the second most common course of DDoS attack.
This occurs when an attack consumes the resources of disquisitional servers and network-based devices, such as a server's operating organisation or firewalls. While those resources are overwhelmed, balancers are loaded. Protocol attacks often include manipulating traffic at layers 3 and 4 of the OSI/RM (the network and transport layers, respectively). This is the 2d most common form of DDoS attack.
In some cases, IT and cybersecurity professionals consider protocol and awarding-based DDoS attacks to be one category.
Gathering Intel: Why You Need to Know Most DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks accept become increasingly problematic, and IT pros need to exist ready.
- Layer 7 attacks take increased through 2020, going into 2021, according to CloudFlare.
- The number of DDoS attacks over 100 GB/south in volume increased nearly tenfold (967%) in Q1 2020, co-ordinate to Comparitech.
- The sheer size of volumetric attacks has increased to overwhelming proportions. CloudFlare too reports that 500 Mbps DDoS attacks accept become the norm for volumetric attacks.
- DDoS attacks are becoming more common. In 2021, ZDNet has reported that DDoS attacks grew by at least 154% in the previous two years.
- Attacks have get more sophisticated. Attackers take combined DDoS with other types of attacks, including ransomware.
- DDoS attackers have adopted sophisticated bogus intelligence (AI) and machine learning methods to aid bear their attacks. For case, DDoS botnets use automobile learning methods to conduct sophisticated network reconnaissance to find the about vulnerable systems. They likewise utilise AI to reconfigure themselves to thwart detection and modify attack strategies. Modern attacks will probable manifest equally both defenders and attackers pit AI-enabled systems confronting each other.
- DDoS attackers accept adopted a blended attack strategy. They combine diverse attack methods with social engineering, credential stealing and physical attacks, making the actual DDoS attack just a single factor in a multifaceted approach.

Tactical Warfare: How DDoS Attackers Avert Detection
DDoS attacks are known to be cunning and therefore tricky to nail down. One of the reasons they are then slippery involves the difficulty in identifying the origin. Threat actors by and large engage in three major tactics to pull off a DDoS set on:
1. Spoofing
By default, IPv4 and IPv6 do not have the ability to authenticate and trace traffic. With IPv4 networks particularly, it is quite uncomplicated to spoof source and destination addresses. DDoS attackers have reward of this consequence past forging packets that take bogus source addresses. Every bit a event, it is possible for an attacker to trick legitimate devices into responding to these packets by sending millions of replies to a victim host that never actually made a request in the first place.
ii. Reflection
Attackers usually want to hide any trace of their involvement in a DDoS set on. To do this, they dispense the default behavior of internet services so that the services finer hide the actual assailant. Services often used in these types of attacks include the thousands of Domain Name System (DNS), Network Fourth dimension Protocol (NTP) and Simple Network Management (SNMP) servers. This is ane of the primary reasons that attackers are attracted to a DDoS strategy. Cyberspace services non only provide the traffic, but they likewise tend to get in more difficult for defenders to trace the origin of the attack because most servers don't keep detailed logs of the services that have used them.
3. Amplification
Amplification is a tactic that lets a DDoS assaulter generate a big amount of traffic using a source multiplier which tin then be aimed at a victim host. Amplification attacks don't use a botnet, it is only a tactic that allows an attacker to send a single forged packet which then tricks a legitimate service into sending hundreds, if not thousands, of replies to a victim network or server.
It's very important to sympathise that DDoS attacks use normal cyberspace operations to deport their mischief. These devices aren't necessarily misconfigured, they are actually behaving as they are supposed to behave. Attackers have simply found a way to exploit this behavior and manipulate it to conduct their DDoS attack.
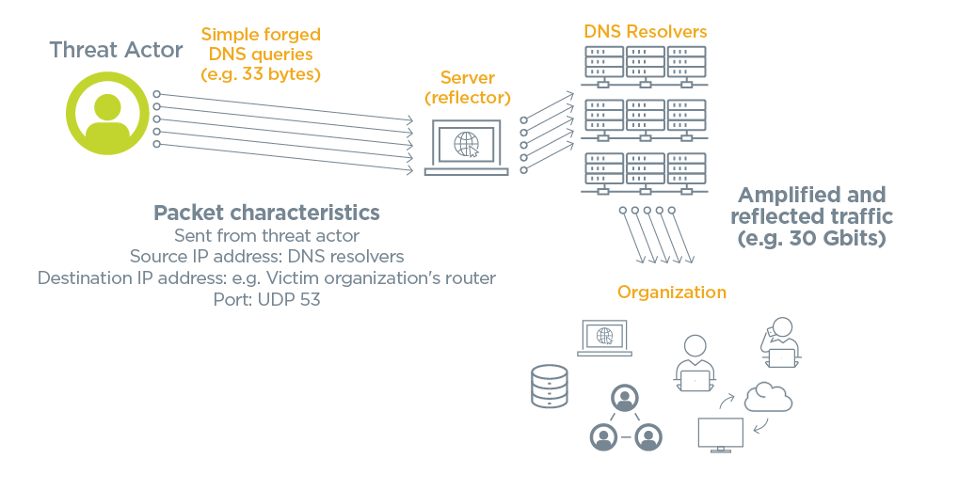
Additionally, network devices and services often become unwitting participants in a DDoS attack. These three tactics accept advantage of the default behavior of network resources worldwide. These resources include:
- Routers
- Switches
- Firewalls
- Load balancers
- Caching servers
- Edge network devices
- Mobile towers (including 4G and 5G)
Battle Elapsing: How Long Do DDoS Attacks Final?
DDoS attacks vary profoundly in length and sophistication. A DDoS attack tin take place over a long flow of time or exist quite brief:
- Long-Term Attack: An attack waged over a period of hours or days is considered a long-term attack. For example, the DDoS assault on AWS caused disruption for iii days before finally being mitigated.
- Burst Set on: Waged over a very short catamenia of fourth dimension, these DDoS attacks just last a minute or even a few seconds.
Don't be deceived. Despite being very quick, burst attacks can actually be extremely damaging. With the advent of internet of things (IoT) devices and increasingly powerful computing devices, information technology is possible to generate more volumetric traffic than always earlier. As a effect, attackers can create higher volumes of traffic in a very curt period of time. A burst DDoS attack is oftentimes advantageous for the assaulter because it is more difficult to trace.
Technological Warfare: Botnets and DDoS Attacks
Botnets, which are vast networks of computers, can be used to wage DDoS attacks. They are unremarkably composed of compromised computers (e.1000., IoT devices, servers, workstations, routers, etc.), or zombies, that are controlled by a central server.
Attackers don't necessarily need a botnet to behave a DDoS attack. Threat actors can simply manipulate the tens of thousands of network devices on the internet that are either misconfigured or are behaving as designed.
Nevertheless, information technology is of import to understand how a botnet-based DDoS assail tin occur.
A More Sophisticated Digital Enemy: The Development of the DDoS Assault
One of the realities of cybersecurity is that most attackers are moderately talented individuals who have somehow figured out how to manipulate a certain network condition or state of affairs. Even though there is often discussion about advanced persistent threats (APT) and increasingly sophisticated hackers, the reality is oftentimes far more mundane.
For example, nearly DDoS attackers simply find a item protocol. They'll discover that they can manipulate the transmission command protocol (TCP) handshake to create a alluvion assault of SYN packets or a particular type of server, such as the memory enshroud daemon (it is often called "Memcached," for memory cache daemon). The Memcached service is a legitimate service frequently used to help speed up web applications. Attackers take often exploited Memcached implementations that are not properly secured, and even those that are operating properly.
Attackers take also discovered that they can compromise IoT devices, such as webcams or baby monitors. But today, attackers take more help. Recent advancements accept given rise to AI and connective capabilities that accept unprecedented potential. Like legitimate systems administrators, attackers now have voice recognition, machine learning and a digital roadmap that can allow them to manipulate integrated devices in your abode or office, such as smart thermostats, appliances and home security systems.
Plan of Assail: The Beefcake of a Botnet-Based DDoS Set on
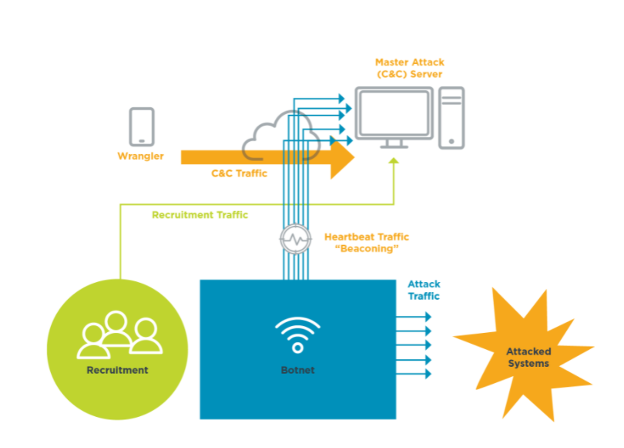
DDoS traffic comes in quite a few different varieties. In the instance of a botnet-based assault, the DDoS threat actor is using a botnet to help coordinate the attack. Agreement the types of traffic will help to select proactive measures for identification and mitigation. Click on the red plus signs to learn more about each blazon of DDoS traffic.
A botnet administrator, or a wrangler, uses a fundamental server or network of servers to command the thousands of members of the botnet. Whenever a wrangler bug a command to control the botnet, this is called Control and Control (C&C) traffic. The actual ambassador is usually far removed from the botnet or C&C server, and the network traffic is commonly spoofed, ofttimes making detection difficult. The C&C operator then issues commands to manipulate network services and devices to create the DDoS assault.
The virtually effective DDoS attacks are highly coordinated. The best analogy for a coordinated attack involves comparing a DDoS botnet to a colony of fire ants. When a fire pismire colony decides to strike, they first take a position and prepare themselves for the attack. Acting under a unmarried directive and without obvious warning, they wait for the betoken and and then act simultaneously.
Whenever a compromised system calls habitation to a C&C server, information technology is said to be beaconing. This traffic passing betwixt a botnet member and its controller often has specific, unique patterns and behaviors. Every bit a issue, in that location is a modest gamble for security analysts to identify this traffic and treat it as a signature to disable a DDoS attack.
- Layer 7: Many modern botnet-based DDoS attacks utilize HTTP floods of GET and POST traffic to incapacitate organizational devices.
- Protocol-based attacks: As indicated above, these attacks can include manipulating diverse protocols, from TCP, UDP and ICMP.
- Amplified: DDoS attackers often use botnets to identify and target internet-based resources that can aid generate massive amounts of traffic.
- Reflected: Reflected attacks take place when the threat actor uses a organisation or series of systems to effectively hibernate the origin.
- OT: Attacks on OT involve physical items that have programming and an IP address associated with them. This could be devices that are used to command electrical grids, pipelines, automobiles, drones or robots.
- IoT: IoT devices contain individual systems that tin can communicate with 1 another or exist integrated. Some examples include video doorbells, smart thermostats, smart watches, IP-enabled light bulbs and printers.
Atypical traffic involves using strategies such every bit reflection and amplification, commonly at the same time.
Modern DDoS attacks combine different attack strategies, including the use of Layer 7, volumetric and fifty-fifty seemingly unrelated methods, such every bit ransomware and malware. In fact, these iii attack types accept become something of a trifecta and are becoming more prominent in the DDoS attack world.
Assembling Weaponry: Tools for Understanding How DDoS Attacks Piece of work
DDoS attacks accept on many forms and are ever evolving to include diverse attack strategies. It'southward essential that IT pros equip themselves with the knowledge of how attacks work.
There are three models that tin help provide insight into the inner workings of DDoS attacks:
- Lockheed Martin Cyber Impale Concatenation : Used to help provide a framework for attack strategies, this model outlines seven steps a hacker might take to conduct a long-term persistent DDoS attack. This model does non business relationship for the employ of botnets to compromise systems.
- Mitre ATT&CK Model : This model profiles existent-earth attacks and provides a knowledge base of known adversarial tactics and techniques to help It pros analyze and prevent future incidents. This model is particularly useful to individuals who wish to defend themselves against DDoS attacks because it allows yous to profile attackers and identify their strategies.
- Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis : The Diamond model helps organizations weigh the capabilities of an adversary and the capabilities of the victim, equally discussed in a CompTIA blog about the iii major cybersecurity models. Even though the Diamond model was created to model bodily intrusions, it is also useful for identifying DDoS attacks.
Every bit an It pro, knowing how to arroyo a DDoS attack is of vital importance as most organizations have to manage an attack of one variety or another over time. Security analysts and threat hunters frequently use the ATT&CK model and the Mitre ATT&CK Navigator to help place conditions that permit for DDoS attacks to be peculiarly successful.
A Cursory History of Major Attacks: DDoS Examples
There have been an exceedingly large number of distributed denial of service attacks over the years. Let's begin with a short list of major DDoS attacks, the motivations behind them and the lasting impact they accept on our digital world. Click on the red plus signs to learn more than well-nigh each of these major DDoS attacks.
The DDoS attacks on Republic of estonia occurred in response to the motility of a politically divisive monument to a armed forces cemetery. To Russian-speaking Estonians, the statue represented Nazi liberation, but to indigenous Estonians, the monument symbolized Soviet oppression. Russian Estonians began rioting, and many were publicly outraged. The week of Apr 27, a barrage of cyberattacks broke out, most of them of the DDoS variety. Individuals used ping floods and botnets to spam and take down many fiscal institutions, government departments and media outlets. This assail is still regarded as one of the most sophisticated to date and is a solid instance of a state-run DDoS attack.
In 2008, the Republic of Georgia experienced a massive DDoS attack, mere weeks before it was invaded by Russia. The attack appeared to be aimed at the Georgian president, taking down several government websites. Information technology was later on believed that these attacks were an effort to diminish the efforts to communicate with Georgia sympathizers. Not long thereafter, Georgia fell victim to Russian invasion. This attack is considered to exist the textbook example of a coordinated cyberattack with concrete warfare. It is studied around the world by cybersecurity professionals and military groups to understand how digital attacks can work in tandem with concrete efforts.
Infamously known every bit the "Attack that Almost Broke the Net," the Spamhaus incident was, at the time, the largest DDoS attack in internet history. The attack was prompted when a grouping named Cyberbunk was added to a blacklist past Spamhaus. In retaliation, the group targeted the anti-spam system that was curtailing their electric current spamming efforts with a DDoS attack that eventually grew to a information stream of 300 Gbps.
The assail was so compromising that it fifty-fifty took downwards Cloudflare, an internet security company designed to gainsay these attacks, for a cursory time.
The DDoS attacks that occurred during Occupy Central were an endeavour to cripple the pro-democracy protests that were occurring in Hong Kong in 2014. Two independent news sites, Apple Daily and PopVote, were known for releasing content in back up of the pro-democracy groups.
Much larger than the Spamhaus attack, Occupy Key pushed data streams of 500 Gbps. This assail was able to circumvent detection by disguising junk packets as legitimate traffic. Many speculate the attack was launched past the Chinese government in an try to squash pro-democracy sentiments.
A massive DDoS assail was launched against the DNS provider Dyn. The attack targeted the visitor's servers using the Mirai botnet, taking down thousands of websites. This attack affected stock prices and was a wake-up call to the vulnerabilities in IoT devices.
The Mirai botnet comprised a drove of IoT-connected devices. The botnet was assembled past exploiting the default login credential on the IoT consumer devices which were never changed by stop users. The attack impacted the services of 69 companies, including powerhouses such and Amazon, CNN and Visa.
One of the largest DDoS attacks in history was launched against GitHub, viewed by many as the most prominent developer platform. At the fourth dimension, this was the largest DDoS attack in history. However, due to precautionary measures, the platform was only taken offline for a matter of minutes.
Attackers spoofed GitHub's IP address, gaining admission to Memcache instances to boost the traffic volumes aimed at the platform. The organization apace alerted support, and traffic was routed through scrubbing centers to limit the damage. GitHub was back up and running within ten minutes.
AWS is well known for existence a leading provider of deject computing services. The company, a subsidiary of the retail behemothic Amazon, sustained an impressive DDoS assault that kept their response teams busy for several days.
Reputed to exist the largest of its kind to appointment, the DDoS attack on AWS in boasts an impressive onslaught of 2.3 Tbps, surpassing the previous leader of 1.seven Tbps. The AWS teams combatted the assail, finally mitigating the threat after a three-mean solar day incursion.
In a foreign turn of events, Google reported a DDoS attack that surpassed the assail on Amazon, claiming it had mitigated a 2.5 Tbps incident years earlier. The set on originated from a country-sponsored group of cybercriminals out of China and spanned six months.
Google divulged the overflowing assault in late 2020 in an endeavor to draw awareness to an increase in country-sponsored attacks. The arrangement did non specify any loss of data due to the incident, merely plans to enhance preventative measures to thwart the rise in attacks.
In contempo years, multiple sectors take reported increasing rates of sector-specific DDoS attacks ranging from manufacturing and retail to financial institutions and even governments. The May, 2021 attack on the Kingdom of belgium government affected more than 200 organizations. But it was specifically designed to disrupt the workings of their authorities. DDoS attacks on specific sectors tin can be used equally political dissent or to signify disagreement with certain business practices or ideals.

The Assaulter Profile: Who Performs DDoS Attacks?
You often meet images of nefarious, dark-hooded individuals to symbolize the malicious threat role player. In reality, these groups of attackers are often well known to authorities and use DDoS tactics to gain influence, disrupt regime and war machine operations or cause people to lose confidence in a market sector, visitor brand or long-established institution.
Regardless of the motivations that power these attacks, hackers can easily be hired to aid launch a DDoS assault—available simply as guns for hire. Individuals or entire commercial groups are available for hire on the night spider web, often under a service model, similar to that of infrastructure as a service (IaaS) or software every bit a service (SaaS). In fact, Radware issued a global security alert in August of 2020 in response to the expanding prevalence of DDoS-for-hire attacks.
What Motivates an Attack: The Reasons Behind a DDoS Attack
In club to thwart DDoS attacks, it's important to empathise what drives the incident. While DDoS attacks vary profoundly in nature when information technology comes to tactics and methods, DDoS attackers besides may have a multitude of motives, including the following.
- Fiscal Motives: DDoS attacks are often combined with ransomware attacks. The attacker sends a message informing the victim that the attack will stop if the victim pays a fee. These attackers are almost oft part of an organized crime syndicate. Today, though, these syndicates can be equally small-scale as a dozen individuals with networking knowledge and extra time on their hands. Sometimes, rival businesses will even carry DDoS attacks on each other to gain a competitive edge.
- Ideological Motives: Attacks are often launched to target oppressive governing bodies or protestors in political situations. A DDoS attack of this kind is often conducted to support a particular political involvement or belief system, such as a religion.
- Country-sponsored Motives: DDoS attacks are often waged to cause confusion for war machine troops or noncombatant populations when political unrest or dissension becomes credible.
- Tactical Motives: In this instance, the DDoS assail is waged every bit part of a larger campaign. In some cases, the campaign includes a physical attack or some other serial of software-based attacks. For example, militaries have been known to combine DDoS attacks with physical ones. Tactical attacks are used to divert attention away from normal Information technology tasks to accept advantage of a dissimilar target – the old bunko cyberattack.
- Concern/Economical Motives: DDoS attacks of this variety aid to get together information or cause damage to item industry sectors. For example, attacks on companies such as Sony, British Airways and Equifax caused consumers to lose faith in unabridged industries.
- Extortion Motives: Other attacks are used to achieve some personal or monetary gain through extorted means.
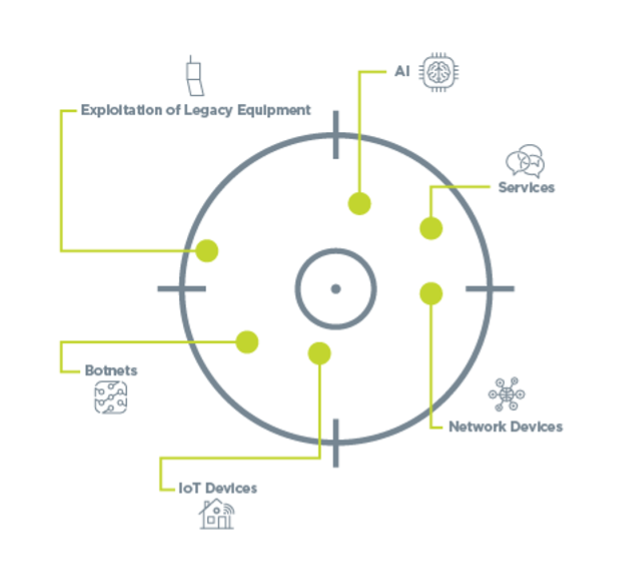
Missile Launched: Tools That Perform DDoS Attacks
Attackers use several devices to target organizations. These are some common tools used in DDoS attacks:
- Services: These include Memcached (used to speed up database and web-based transactions), the DNS server, the NTP and the SNMP.
- Network Devices: Network devices include items such as routers and switches.
- Botnets: Collections of compromised systems commonly used in DDoS attacks.
- IoT Devices: Weaknesses in continued devices can exist exploited by cybercriminals, turning them into zombies. The infamous Mirai botnet was utilized to launch a series of attacks using unsecured baby monitors.
- AI: Artificial intelligence is being used by hackers to modify code during a DDoS attack automatically so the attack remains constructive despite safeguards.
- Exploitation of Legacy Equipment: Older hardware is often exposed to more vulnerabilities and is routinely targeted and exploited.
The Role of Recon: Keeping Rails of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attackers get more and more savvy every twenty-four hour period. Attacks are expanding in size and duration, with no signs of slowing. Organizations demand to keep a finger on the pulse of incidents to sympathize how susceptible they may be to a DDoS attack.
Here are some resource that can assistance you keep track of the latest DDoS attacks:
- Mazebolt Worldwide Listing of DDoS Attacks : This resources provides a running listing of attacks with information such every bit appointment, country of origin, reanimation, assail details and even links to press information about the incident.
- Cybersecurity Threat Intelligence (CTI) Sharing Resources:
- CompTIA ISAO : CompTIA maintains an organization dedicated to sharing intelligence related to threats and providing actionable insight for mitigating and solving cybersecurity challenges.
- U.Due south. CISA Automated Indicator Sharing : The tool provided by CISA enables real-fourth dimension sharing of cyberthreat data to assist limit the prevalence of attacks.
- FBI Infragard : A partnership between the FBI and private sectors, InfraGard supports the sharing of information about attacks and mitigation techniques.
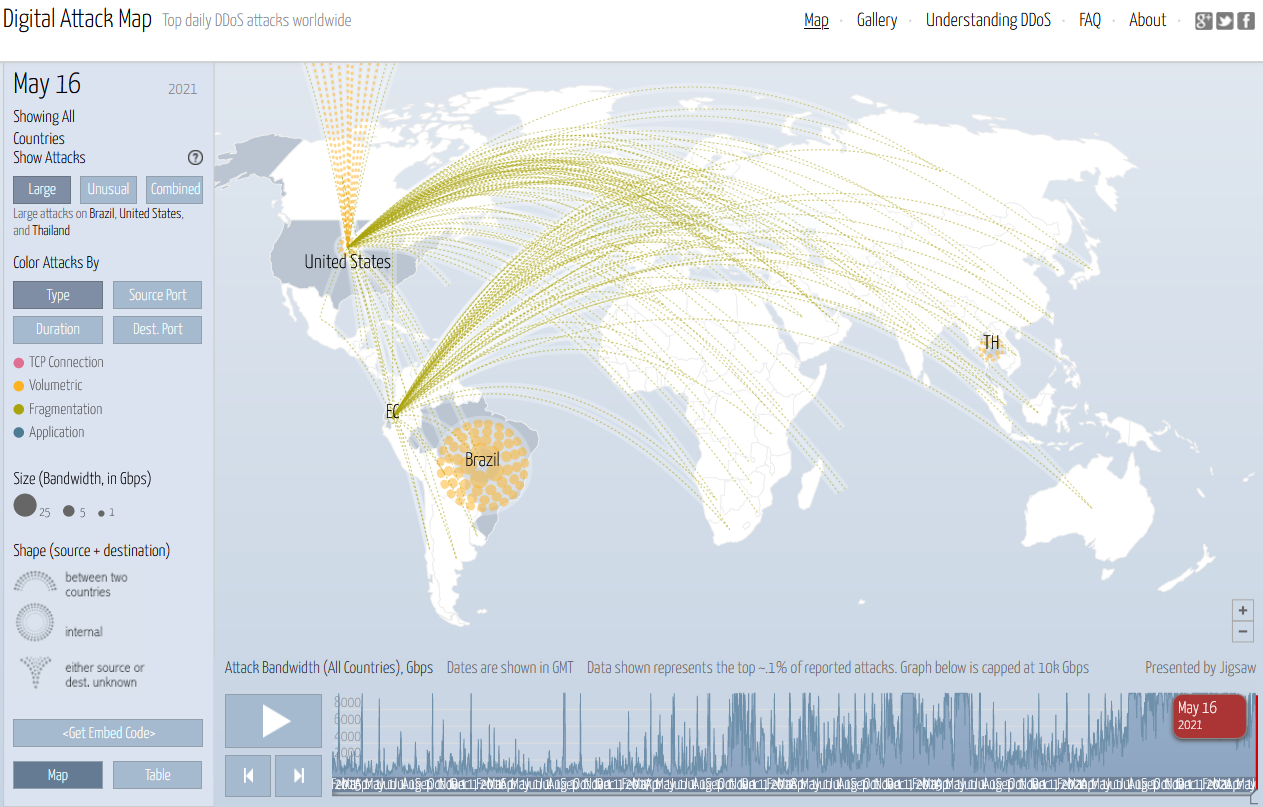
- Digital Assail Map : This map shows a live feed of DDoS attacks beyond the world and allows yous to filter by type, source port, duration and destination port.
- AlienVault Open Threat Exchange : This threat intelligence customs provides free access to threat indicators and allows for sharing of threat research with others.
- Threatbutt Internet Hacking Attack Attribution Map : This map provides real-fourth dimension tracking of DDoS attacks around the globe.
- Is Information technology Downward Correct At present? : This resources is a proficient identify to start when you suspect an assault. Cheque to see whether a website is down by inbound the domain and this tool volition return immediate results.

Target Identified: What Do DDoS Attackers Target the Well-nigh?
While organizations in whatever industry are vulnerable, these sectors are bailiwick to DDoS attacks almost oft:
- Wellness intendance
- Authorities
- Internet service providers (ISPs)
- Cloud service providers
Eyes on the Enemy: Identifying DDoS Attacks
From a tactical DDoS mitigation standpoint, one of the main skills y'all demand to take is design recognition. Existence able to spot repetitions that signify a DDoS attack is taking place is key, specially in the initial stages. Automated applications and AI are often used every bit helpers, simply generally companies need a skilled IT professional to differentiate between legitimate traffic and a DDoS set on.
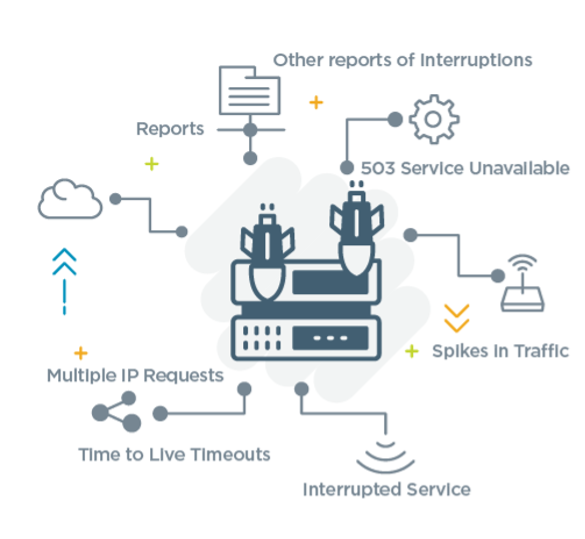
Workers often look for the following warning signs that a DDoS attack is taking identify:
- Reports from existing mitigation devices (e.1000., load balancers, deject-based services)
- Customers report slow or unavailable service
- Employees utilizing the same connection likewise experience problems with speed
- Multiple connection requests come in from a specific IP address over a brusque amount of time
- You receive a 503 service unavailable error when no maintenance is existence performed
- Ping requests to applied science resources fourth dimension out due to Time to Live (TTL) timeouts
- Logs evidence an abnormally huge spike in traffic
Responding to a Threat: Response Techniques, Services and Strategies Used to Mitigate a DDoS Attack
DDoS mitigation is quite different than mitigating other cyberattacks, such as those originating from ransomware. DDoS attacks are mostly mitigated by devices and services that have been enabled to handle these types of attacks. For example, today'due south load balancers are sometimes able to handle DDoS attacks by identifying DDoS patterns and then taking activity. Other devices can be used as intermediaries, including firewalls and dedicated scrubber appliances.
When trying to mitigate a DDoS assault, you want to focus on placing services and devices between your network and the systems existence used to set on you. Because attackers generate DDoS traffic by exploiting legitimate network and internet behavior, any connected device or server is vulnerable to an attack because it isn't recognized as malicious in nature. You must create an intermediate mitigation solution to answer to that attack instead. In a ransomware or malware attack, security professionals generally solve the problem by upgrading the software on end points or restoring from backup.
Acting on a Threat: 5 Steps for DDoS Attack Response
Typical steps for responding to a DDoS attack include:
1. Detection
Early detection is disquisitional for defending against a DDoS attack. Look for alert signs, provided in a higher place, that you may be a target. DDoS detection may involve investigating the content of packets to discover Layer seven and protocol-based attacks or utilizing charge per unit-based measures to detect volumetric attacks. Rate-based detection is usually discussed start when it comes to DDoS attacks, merely most effective DDoS attacks are not blocked using rate-based detection.
2. Filtering
A transparent filtering procedure helps to drib the unwanted traffic. This is done by installing effective rules on network devices to eliminate the DDoS traffic.
3. Diversion and redirection:
This step involves diverting traffic so that information technology doesn't affect your disquisitional resources. Y'all can redirect DDoS traffic past sending information technology into a scrubbing center or other resource that acts as a sinkhole. It is typically recommended that yous transparently communicate what is taking identify then that employees and customers don't demand to change their behavior to accommodate slowness.
iv. Forwarding and assay:
Understanding where the DDoS assail originated is important. This knowledge can assistance yous develop protocols to proactively protect against future attacks. While it may be tempting to try and kill off the botnet, it can create logistical issues and may effect in legal ramifications. More often than not, it is non recommended.
five. Alternate delivery
It is possible to use alternate resources that can almost instantaneously offer new content or open up up new networking connections in the event of an assail.

One of the best means to mitigate a DDoS attack is to reply equally a team and interact during the incident response process. The steps outlined above tin only be achieved through a combination of services, devices and individuals working together. For case, to mitigate Layer 7 DDoS attacks it is oftentimes necessary to exercise the following:
- Detection: Organizations will use a combination of security analyst and penetration activities to identify Layer vii attack patterns. A penetration tester more often than not simulates the DDoS assail, and the security analyst will heed carefully to identify unique characteristics.
- Traffic filtering: Use scrubbing centers and services to aid redirect and contain harmful traffic.
- Layer 7 control: CAPTCHAs and cookie challenges are often used to determine if a network connection request is originating from a bot or legitimate user.
- Forwarding of packets to a security professional for further assay: A security analyst volition engage in pattern recognition activities and then recommend mitigation steps according to their findings.
- Alternating delivery during a Layer 7 set on: Using a CDN (content commitment network) could assist support additional uptime when your resource are combatting the attack. It is important to annotation that mitigation devices can experience problems. It may non exist properly updated or configured, and tin actually become role of the problem during a DDoS attack.
Limiting the Damage: DDoS Mitigation Techniques
Once you know you are facing a DDoS assault, it'due south time for mitigation. Ready for the fight!
| Physical devices | Managing concrete devices during a DDoS attack has largely remained a dissever category from other mitigation efforts. Frequently called appliances, physical devices are kept carve up considering DDoS patterns and traffic are and so unique and difficult to properly identify. Even so, devices can exist very effective for protecting modest businesses from DDoS attacks. |
| Cloud scrubbing devices | Often called scrubbing centers, these services are inserted between the DDoS traffic and the victim network. They take traffic meant for a specific network and route it to a different location to isolate the damage abroad from its intended source. The scrubbing center cleans the data, merely allowing legitimate business traffic to laissez passer on to the destination. Examples of scrubbing services include those provided by Akamai, Radware and Cloudflare. |
| Multiple cyberspace service connections | Because DDoS attacks ofttimes seek to overwhelm resources with traffic, businesses sometimes use multiple Isp connections. This makes it possible to switch from 1 to another if a unmarried ISP becomes overwhelmed. |
| Blackness hole | This DDoS mitigation technique involves using a cloud service to implement a strategy known equally a data sink. The service channels bogus packets and floods of traffic to the data sink, where they can practice no impairment. |
| Content commitment network (CDN) | This is a group of geographically distributed proxy servers and networks oftentimes used for DDoS mitigation. A CDN works as a unmarried unit to provide content speedily via multiple backbone and WAN connections, thus distributing network load. If i network becomes flooded with DDoS traffic, the CDN can evangelize content from another unaffected group of networks. |
| Load balancing servers | Mostly deployed to manage legitimate traffic, load balancing servers can also be used to thwart DDoS attacks. It pros can utilize these devices to deflect traffic away from certain resource when a DDoS attack is under way. |
| Web application firewall (WAF) | Used to filter and monitor HTTP traffic, WAFs are often used to assistance mitigate DDoS attacks and are unremarkably part of cloud-based services such as AWS, Azure or CloudFlare. While sometimes constructive, a dedicated device or cloud-based scrubber is oftentimes recommended instead. A WAF focuses on filtering traffic to a specific web server or application. But a truthful DDoS attack focuses on network devices, thus denying services eventually meant for the spider web server, for example. All the same, there are times when a WAF can be used in conjunction with additional services and devices to answer to a DDoS attack. |
Virtually all DDoS mitigation devices on the market use the same five mechanisms:
- Signature
- Behavioral or SYN flood
- Rate-based and geolocation: Equally mentioned higher up, this is not usually reliable.
- Botnet detection/IP reputation lists: The success of using lists will vary depending on the quality of your lists.
- Claiming and response
Weapons at the Fix: DDoS Mitigation Services
Hundreds of organizations provide devices and services intended to help you prevent or combat a DDoS attack. A modest sample of these services and devices is shown below.
| DDoS Mitigation Vendor | Services Offered |
| AWS Shield | Offers protection against Layer 3 and Layer four attacks. Available to all customers at no extra charge. Additional protection for Layer seven attacks is bachelor for a fee. |
| Neustar DDoS Protection | Solutions include cloud-based, on-premise and hybrid protection completely focused on thwarting DDoS attacks. |
| Cloudflare DDoS Protection | Layer three, four and 7 services for gratuitous, as well as more sophisticated DDoS protection services for a fee. |
| Akamai | A highly respected service for help against volumetric DDoS attacks. Akamai owns many sites around the world to aid identify and filter traffic. |
| AppTrana | Focuses on Layer 7 every bit well as volumetric (Layer 3 and 4) DDoS traffic. |
| Alibaba DDoS | Specializes in mitigating volumetric attacks. |
A Coordinated Defence: Best Practices for DDoS Response
Click the cherry plus signs for more details on the 8 means you can fix for a DDoS attack.
If y'all don't have a defined security policy, then creating 1 is the first pace. If your policy is older or hasn't considered modern DDoS methods and issues, it'due south fourth dimension to make a few changes.
Business-disquisitional services are those that would cause operational delays if affected. These might include systems such equally database, web, commerce server, customer relationship management (CRM), custom programming, AI, machine learning, streaming and data collection, among others. It may also be necessary to outline all concern-critical applications running on your spider web servers. You tin and so make decisions based on the sample matrix, located below.
Store mission-critical data in a CDN to allow your organization to reduce response and recovery time.
Larger organizations will want to take multiple ISPs gear up in case i becomes flooded with traffic or tin can't provide an essential filtering service in time. Equally an alternate or complementary solution, y'all could as well appoint a third-party scrubbing service that filters out DDoS traffic.
It is important to dorsum up server resources, every bit well as workstations and other devices.
A DDoS training scheme will e'er identify the adventure involved when specific resources become compromised.
The last thing an organization wants to do is assign responsibleness for DDoS response during or after an actual attack. Assign responsibility earlier an assault happens.
Similar to other areas of expertise, the best way to know how to respond to a DDoS attack is to practice. Schedule dedicated grooming sessions and practise combatting attacks in a controlled environs.
Training at the Ready: The Exercise's and Don'ts of Responding to a DDoS Attack
When dealing with a DDoS attack, at that place are certain best practices that tin help continue a situation under control. Observe these DDoS attack exercise'south and don'ts.
| What to Practise When Dealing with a DDoS Attack | What Non to Exercise When Dealing with a DDoS Attack |
|---|---|
| Overcommunicate with management and other workers. Leadership needs to be informed and involved and so that the necessary steps are taken to limit impairment. | Overcommunicate with the public. To limit damage to your brand's reputation and ensure yous have the assail contained, only provide necessary data to the public. |
| Delegate tasks. A DDoS attack ways all easily on deck. Enlist other IT pros to report dorsum and follow up with quick updates. | Presume that it is someone else'southward responsibility to handle the attack. These attacks must be dealt with quickly, and waiting to hand off responsibleness can cost valuable time. |
| Focus on root-crusade analysis. Uncovering the cause of the assault tin can exist vital when attempting to tedious the progression. | Try to solve the trouble lone. DDoS attacks can escalate very quickly. Enlisting others in your mitigation efforts will help curb the assault more quickly. |
| Deport mock exercises for DDoS attacks. This may involve planned or surprise exercises to properly brainwash It pros, staff and management on response activities. | Make the assumption that IT pros, staff or management know what to exercise during a DDoS assault. Without proper preparation, these attacks can be damaging, and many employees lack the practical skills to counteract the hack. |
| Piece of work with ISPs, cloud providers and other service providers to decide the costs related to the DDoS set on. Go a report from all providers. To move past the attack, y'all need to know exactly what you lot are dealing with and have documentation to illustrate it. | Assume old reports are still valid. Whatever reports older than vi months or that involve information from before a company merger or major business organization change should not be considered sound data. |
A Formidable Strategy: DDoS Mitigation Matrix
With so many as-a-service options, it tin be difficult to know which services to engage as part of an effective DDoS prevention strategy. This DDoS mitigation matrix should assistance you understand how to place your services appropriately.
| Service | Location | Mitigation Tactic |
|---|---|---|
| Spider web server | Company server room | Installed on the on-premise Web Application Firewall (WAF) |
| Database server | Public deject | Load balancer, cloud-based DDoS mitigation server |
| Credit card-accepting commerce server | Private cloud | Load balancer, cloud-based DDoS mitigation server, alternate Internet service provider |
| Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) hosts for end users | Public deject | Cloud-based DDoS protection service, alternate ISP, |
| Network infrastructure | On-premise | Multiple alternate ISPs, cloud scrubbing service |
Your matrix would, of course, vary according to your business-critical resources. It's also important to remember that outsourcing yet requires internal support. If yous purchase a costly mitigation device or service, you need someone in your organization with plenty knowledge to configure and manage it.
There are times when it is useful to simply outsource for a skillset. But, with DDoS attacks and others, it is always all-time to have internal expertise. Otherwise, you may end up with a situation where an outsourced expert has made changes to your DDoS protection suite, but then moves on to another arrangement.
IT Pro Skills and Tools for DDoS Management
Every bit an IT pro, you lot can accept steps to help ready yourself for a DDoS attack. Check out the following skills and tools that can aid yous successfully manage an incident.
Attack Basics: The Skills You Need to Manage DDoS Attacks
Employers will want to know that you are armed with the skills necessary for combatting a DDoS attack. Calculation these skills to your toolset will help illustrate your power to thwart attacks.
- Develop effective planning and management of products and applications.
- Communicate clearly during a response.
- Demonstrate ability to piece of work with deject and ISP providers to tackle difficult situations and troubleshoot problems.
- Illustrate effectiveness in red teaming and blue teaming drills.
- Proactively act equally a threat hunter to identify potential threats and empathize which systems are critical to business operations.

Standards such as the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication (SP) 800-61 provide a helpful foundation for knowing how to respond to attacks of diverse types. The IT industry also uses the ISO/IEC 27035-ane:2016 standard as a guideline for incident response procedures. As a full general rule, organizations with a reputation for responding well to incidents tend to utilise such standards every bit helpful guidelines, rather than absolute rules to follow.
IT pros can also do good from seeing demonstrations of attacks to learn how information behaves in particular situations. Take the time to view demonstrations of the following attacks:
- Ransomware
- DDoS
- Browser-based threats

DDoS Boot Army camp: DDoS Education Options for Information technology Pros
Ongoing education is essential for any Information technology pro. Technology advances every day, and IT pros that stagnate will eventually be deemed unnecessary equally legacy systems dice off and new platforms have their place. To remain relevant, information technology's of import to continue educating yourself.
The standards and practices taught in the industry will besides aid y'all and your arrangement respond to DDoS attacks. One manner to obtain the advisable level of noesis is to learn the standards and best practices covered by the Information technology certifications found in the CompTIA Cybersecurity Pathway.
| Endpoints | Cloud | Servers | Red Team | Bluish Squad | Network Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | | | | | |
Download the exam objectives for the higher up CompTIA exams to see what'due south covered and decide which one is right for yous.
Want to know more than about DDoS attacks and stay up to appointment on the latest in cybersecurity? Subscribe to CompTIA'due south IT Career News for weekly digests and a monthly newsletter dedicated to cybersecurity, cloud computing, computer networking, tech support and more than.
Terms to Know
- ACK: Acknowledgement packet
- DNS: Domain Name Arrangement
- HTTP: Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
- ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol
- OSI/RM: Open up Systems Interconnection/Reference Model
- Incident response: Steps to accept when managing a DDoS attack.
- SYN: Synchronize bundle
- SYN flood: Where an attacker manipulates the three-mode TCP handshake to create a DDoS attack.
- TCP: Transmission control protocol
- TCP handshake: A three-step procedure that occurs whenever two computers communicate with each other at the first of a TCP session. Besides known every bit the TCP three-way handshake.
- UDP: User Datagram Protocol
5 Steps to DDoS Response
Download CompTIA'southward free Quick Response Guide to DDoS Attacks with tips and tricks for mitigation and response so you're prepare to protect your arrangement at a moment's find.
Download the Guide
Read more most Cybersecurity.
Source: https://www.comptia.org/content/guides/what-is-a-ddos-attack-how-it-works
Posted by: simpsonprinnexparm.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Scenarios Illustrates Denial Of Service (Dos), A Type Of Security Loss?"
Post a Comment